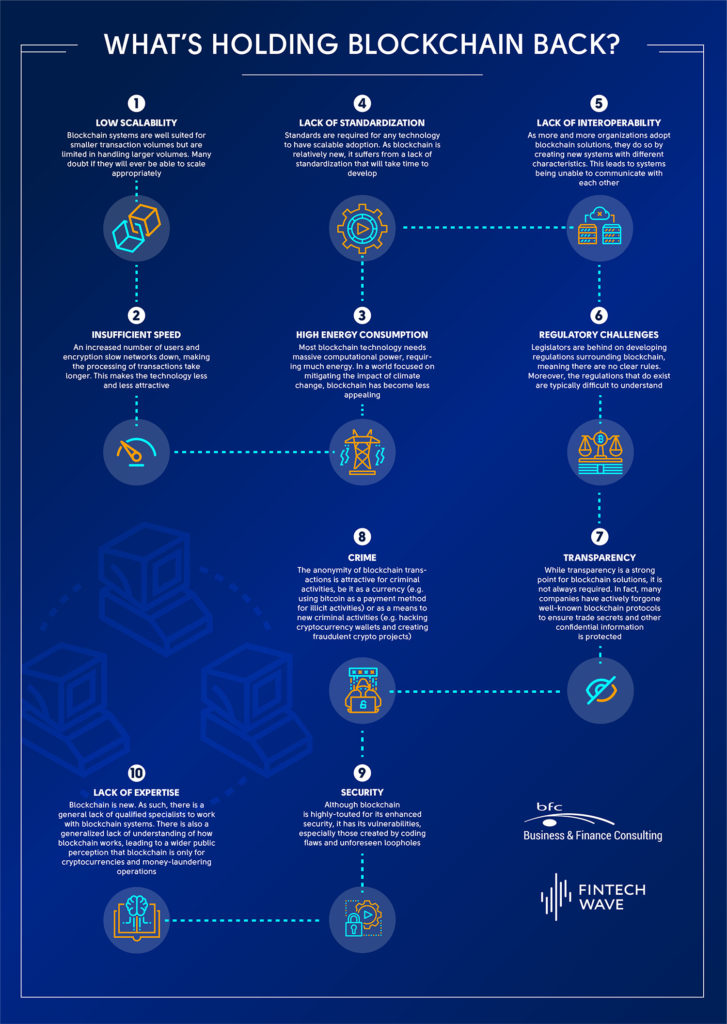
Though blockchain has many advantages, it still has a lot of growing pains to go through before its full potential can be unlocked. Here are a few of the main challenges blockchain solutions are facing.
- Low Scalability – blockchain systems are well suited for smaller transaction volumes but are limited in handling larger volumes. Many doubt if they will ever be able to scale appropriately.
- Insufficient Speed – an increased number of users and encryption slow networks down, making the processing of transactions take longer. This makes the technology less and less attractive.
- High Energy Consumption – most blockchain technology needs massive computational power, requiring much energy. In a world focused on mitigating the impact of climate change, blockchain has become less appealing.
- Lack of Standardization – standards are required for any technology to have scalable adoption. As blockchain is relatively new, it suffers from a lack of standardization that will take time to develop.
- Lack of Interoperability – as more and more organizations adopt blockchain solutions, they do so by creating new systems with different characteristics. This leads to systems being unable to communicate with each other.
- Regulatory Challenges – legislators are behind on developing regulations surrounding blockchain, meaning there are no clear rules. Moreover, the regulations that do exist are typically difficult to understand.
- Transparency – while transparency is a strong point for blockchain solutions, it is not always required. In fact, many companies have actively forgone well-known blockchain protocols to ensure trade secrets and other confidential information is protected.
- Crime – the anonymity of blockchain transactions is attractive for criminal activities, be it as a currency (e.g. using bitcoin as a payment method for illicit activities) or as a means to new criminal activities (e.g. hacking cryptocurrency wallets and creating fraudulent crypto projects).
- Security – although blockchain is highly-touted for its enhanced security, it has its vulnerabilities, especially those created by coding flaws and unforeseen loopholes.
- Lack of Expertise – blockchain is new. As such, there is a general lack of qualified specialists to work with blockchain systems. There is also a generalized lack of understanding of how blockchain works, leading to a wider public perception that blockchain is only for cryptocurrencies and money-laundering operations.
 BFC Bulletins Monthly News Digest
BFC Bulletins Monthly News Digest